
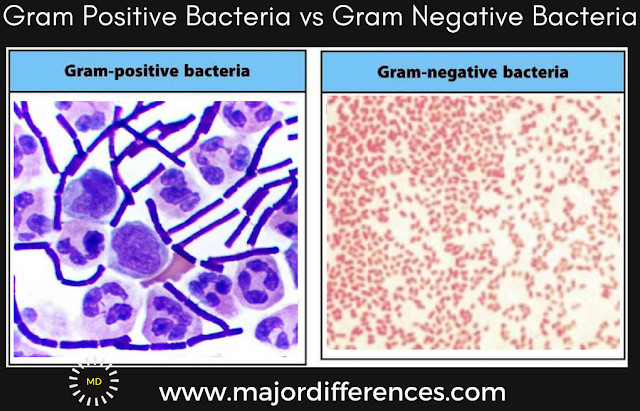
pyogenes is a type of β-hemolytic Streptococcus. Streptococcus is an example of a Gram + infection and is identified by its ability to lyse, or breakdown, red blood cells when grown on blood agar. Streptococcus, the name which comes from the Greek word for twisted chain, is responsible for many types of infectious diseases in humans.
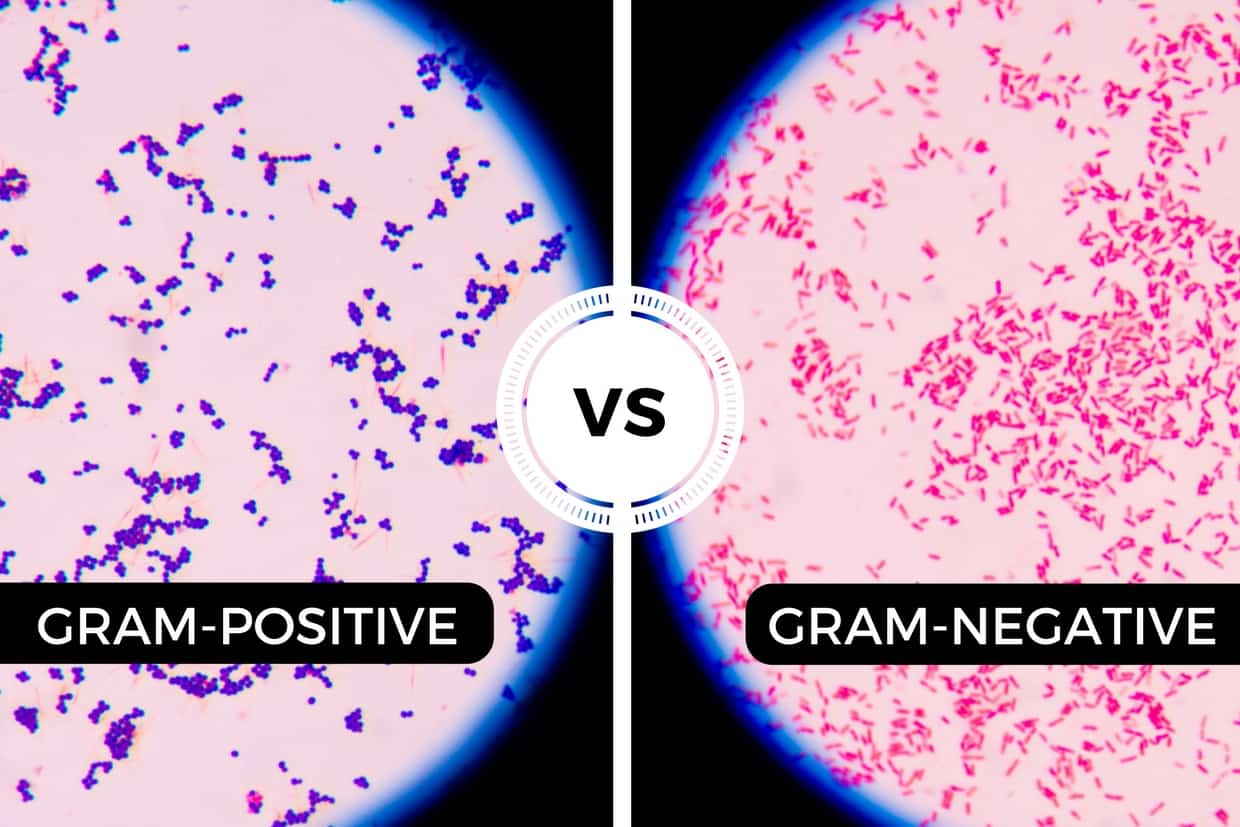
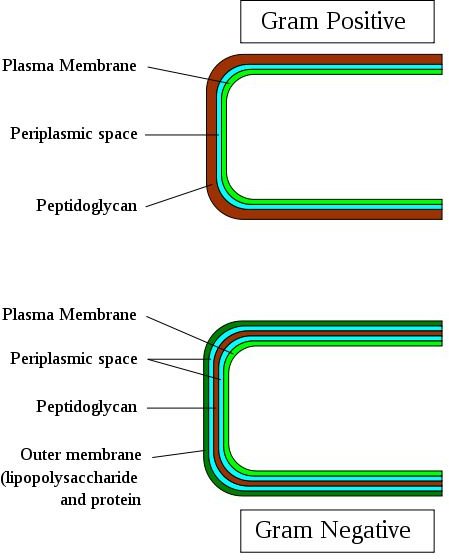
Sample Gram Positive Infections Figure 3.1 Gram Stain Specimen Streptococcus Identification of bacteria as gram positive or gram negative assists the healthcare provider in quickly selecting an appropriate antibiotic to treat the infection. Utilizing gram stain allows microbiologists to look for characteristic violet (Gram +) or red/pink (Gram -) staining patterns when they examine the organisms under a microscope. Gram stains are useful for quickly identifying if bacteria are “gram positive” or “gram negative,” based on the staining patterns of their cellular walls. Gram NegativeĪ gram stain is another type of test that is used to assist in classification of pathogens. Sometimes a patient may begin antibiotic treatment for an infection, but will be switched to a different, more effective antibiotic based on the culture and sensitivity results. If the organism shows resistance to the antibiotics used in the test, those antibiotics will not provide effective treatment for the patient’s infection. A sensitivity analysis is often performed to select an effective antibiotic to treat the microorganism. Clinical microbiologists subsequently monitor the culture for signs of organism growth to aid in the diagnosis of the infectious pathogen. Once culture samples are collected, they are then incubated in a solution that promotes bacterial or fungal growth and spread onto a special culture plate. Antibiotic administration prior to a culture can result in a delayed identification of the organism and complicate the patient’s recovery. Nurses are commonly responsible for the collection of culture samples and must be conscientious to collect the sample prior to the administration of antibiotics. These culture samples are commonly collected from a patient’s blood, urine, sputum, wound bed, etc. A culture is a test performed to examine different body substances for the presence of bacteria or fungus. When a patient presents signs or symptoms of an infection, healthcare providers will begin the detective work needed to identify the source of the infection. Each of these topics will be discussed in more detail below, along with the issue of drug resistance. In addition to antibiotics, antimicrobials also include medications used to treat viruses and fungi.
Finally, the mechanism of action is also considered in the selection of an antibiotic. Additionally, antibiotics may be bacteriostatic or bactericidal in terms of how it targets the bacteria. Antimicrobials may be classified as broad-spectrum or narrow-spectrum, based on the variety of bacteria they effectively treat. Pathogens, when overgrown, can cause significant health problems or even death for your patients.īacteria may be identified when a patient has an infection by using a culture and sensitivity test or a gram stain test. A pathogen is defined as an organism causing disease to its host. Most bacteria are harmless or considered helpful, but some are pathogens. Bacteria are found in nearly every habitat on earth, including within and on humans. Open Resources for Nursing (Open RN) Basic Concepts Related to Antimicrobial Therapyīefore we learn about medications that are used to treat infections in our patients, we must first understand the basics of microbiology.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
